Understanding cloud services is crucial due to their myriad benefits. The term "cloud" might vary in definition based on the context or its users. Broadly, it refers to an environment that offers seamless access to apps, content, and data from any device. From a provider's standpoint, cloud infrastructure offers an environment for remotely setting up virtual machines. At its core, it's built on hardware and is complemented by specialized software known as a hypervisor. Essentially, a hypervisor leverages virtualization to run software on physical hardware.
The History Of The Emergence Of Cloud Platforms
The essence of cloud technology can be distilled into three fundamental concepts:
- Providing services like computing or data storage,
- Multiple users sharing the same resources,
- Service accessibility over a network.
Professor John McCarthy predicted as early as 1961 that computers would evolve into a service. In 1967, IBM introduced a virtualized OS, enabling multiple users to access the same files. By 1969, the US Department of Defense had initiated the ARPANET, founded on the TCP/IP protocol. Cloud technology saw a surge in advancement during the 1990s. As the internet began its rapid expansion, over a million computers connected online. The dawn of modern cloud services can be traced back to 2002, with the inception of AWS's public cloud.
First Generation of Clouds
At this stage, the traditional definition of the cloud emerged as a centralized infrastructure in data centers. These centers housed vast computing and data storage resources. In such a setup, providers managed the backend, and users directed all their queries to the cloud using a traditional two-tier architecture.
Second Generation of Clouds
During the cloud's second development phase, service offerings surged due to increased provider choices, boosting competition. With resource tracking available, trust in cloud technology grew. Beyond the traditional pricing, a pay-as-you-go model was introduced. Real-time streaming services processed data in the cloud, and microservice architecture was adopted for cloud app development, aided by the 2014 launch of container services in the cloud.
Why the Name "Cloud Services"?
The term stems from the ability to access resources over an internet connection. Users can tap into these resources irrespective of their geographic location or device type. This accessibility renders data and resource usage more adaptable, expandable, and user-friendly. Core principles of cloud services include:
- frontend;
- backend;
- network.
The combination of the three components together defines the architecture of cloud services.
Identifying Cloud Service Providers
Companies that provide cloud services to end users are called cloud providers. They focus on the development of public clouds, can implement private clouds based on client requests, and also offer various associated services under the PaaS and SaaS models. We will delve deeper into these types below.
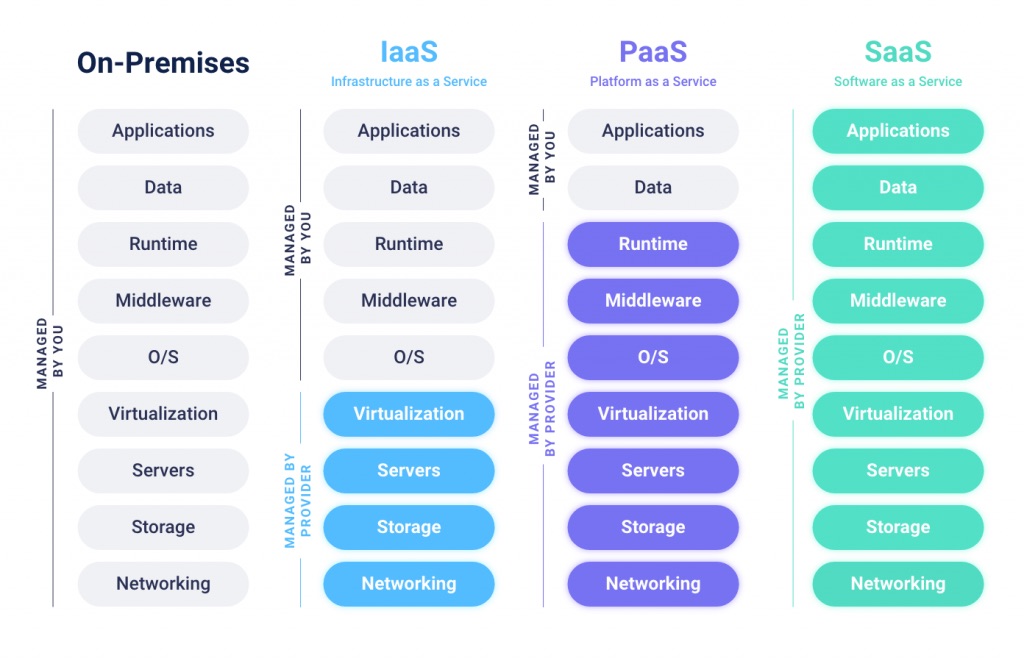
Types of cloud services: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): This model involves a cloud provider supplying the client with raw computing resources in the guise of virtual machines or cloud servers. Here, clients set up the required services on the rented infrastructure.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Under this model, users are presented with pre-established and configured virtual machines tailored for specific tasks. In some instances, clients might lack access to certain layers of the PaaS offering.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): This model represents the epitome of ready-to-use services. It encompasses pre-configured programs in the cloud vital for specific applications. Here, users are absolved from setup responsibilities.
You can delve deeper into these types in our previous article. A link will be provided at the conclusion.
Platform Cloud Services and Tools for Cloud Operations
When discussing PaaS, it's important to highlight services that enhance the speed of infrastructure development and operation:
- Serverless: Allows application creation and execution without managing server or virtual machine infrastructure.
- DBaaS: This PaaS service offers a ready-to-use database cluster in the cloud, removing the hassle of extra configuration.
- KaaS: Offers users a managed container orchestration system without needing to handle the IT infrastructure.
- IaC (Infrastructure as Code): Automates infrastructure management through code rather than manual setup. This means developers don't manually handle servers, OS, or storage during app development or deployment.
Cloud Types
As cloud technology evolved, several distinct types emerged:
Public clouds, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and iCloud, allow multiple users on a single virtualization host, effectively making them share resources.
In contrast, private clouds ensure that resources aren't shared. A user has full access to cloud vCPUs. Companies can either construct their private cloud on their infrastructure or lease it. Another option is to lease a private cloud setup from a specialized provider.
Hybrid clouds seamlessly integrate the benefits of both private and public clouds, offering a combination that's gaining traction in the industry.
Other Cloud Types
Multi-cloud involves a company using resources from multiple cloud providers, often for reasons related to geographic distribution and enhanced infrastructure reliability.
The Community Cloud model is a cloud service accessible only to specific groups or organizations. Think of it as a semi-public cloud restricted to select entities.
Advantages Of Cloud Services
The primary benefits include:
- Flexibility and scalability.
- Resource conservation.
- High security standards.
- Constant availability.
How Businesses Use Cloud Computing
Why is cloud computing essential for businesses? Cloud computing offers transformative solutions for businesses, addressing several core challenges:
- It eliminates the constant need to recruit and retain specialized IT personnel dedicated to maintaining and troubleshooting infrastructure.
- It reduces the financial burden of continuously purchasing, upgrading, and maintaining physical equipment, allowing businesses to scale seamlessly as they grow.
- Most importantly, by leveraging cloud services, businesses can significantly enhance the security of their data and equipment, benefiting from the advanced security protocols and regular updates provided by cloud providers.
Migrating to Cloud Servers
The migration process includes:
- Auditing your current service architecture.
- Selecting a suitable provider.
- Registering within the provider's control panel.
- Setting up access to servers and applications.
- Migrating data from local servers to the cloud.
- Ensuring the cloud services' security.
- Training employees on cloud-based technologies.
3HCloud offers assistance with migration to our cloud infrastructure.
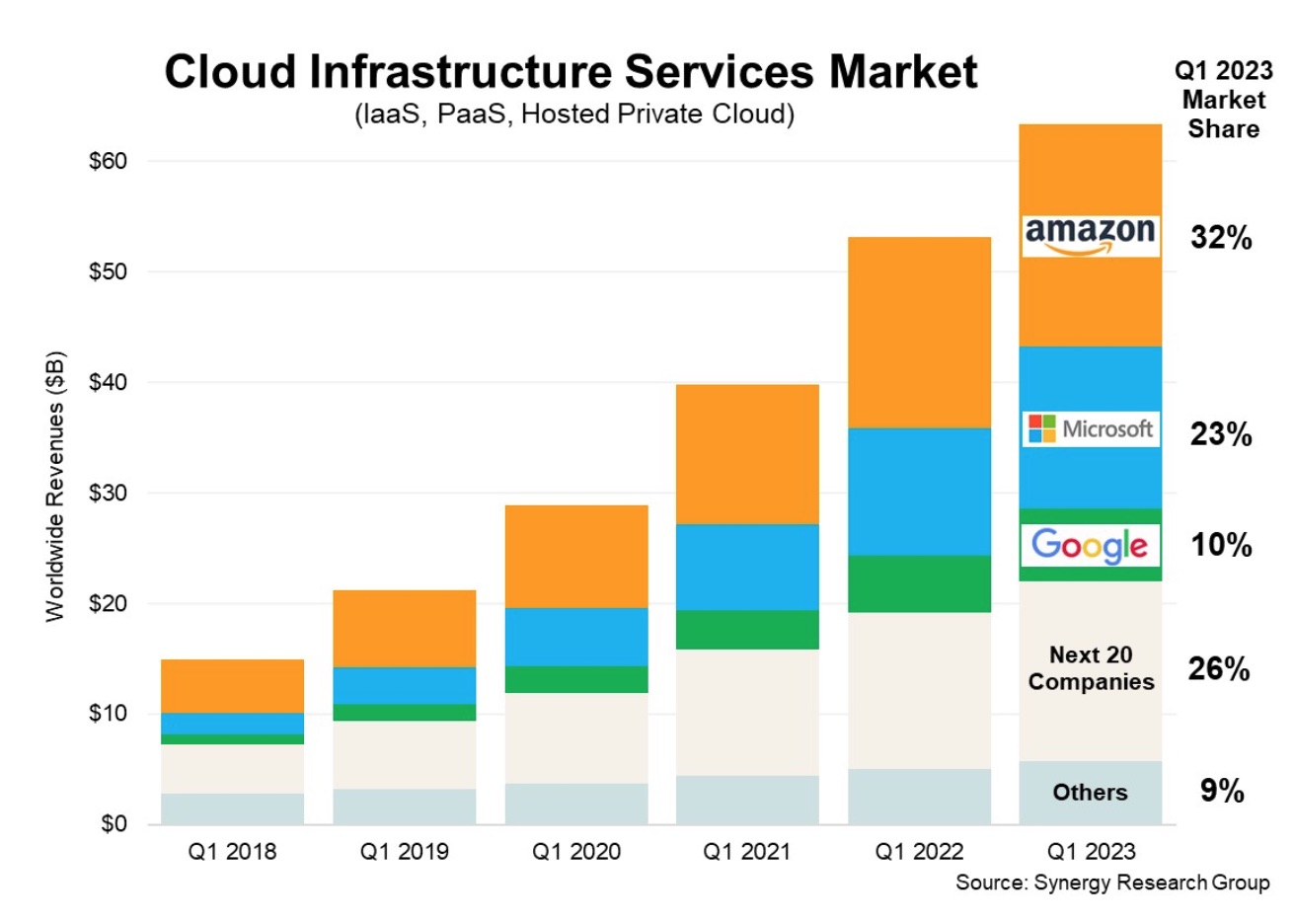
Global Cloud Services Market Overview
Based on data from Synergy Research Group for Q1 2023, the leading market cloud providers are:
- AWS (Amazon Web Services) holding a 32% market share,
- Microsoft Azure at 23%,
- Google Cloud capturing 10%.
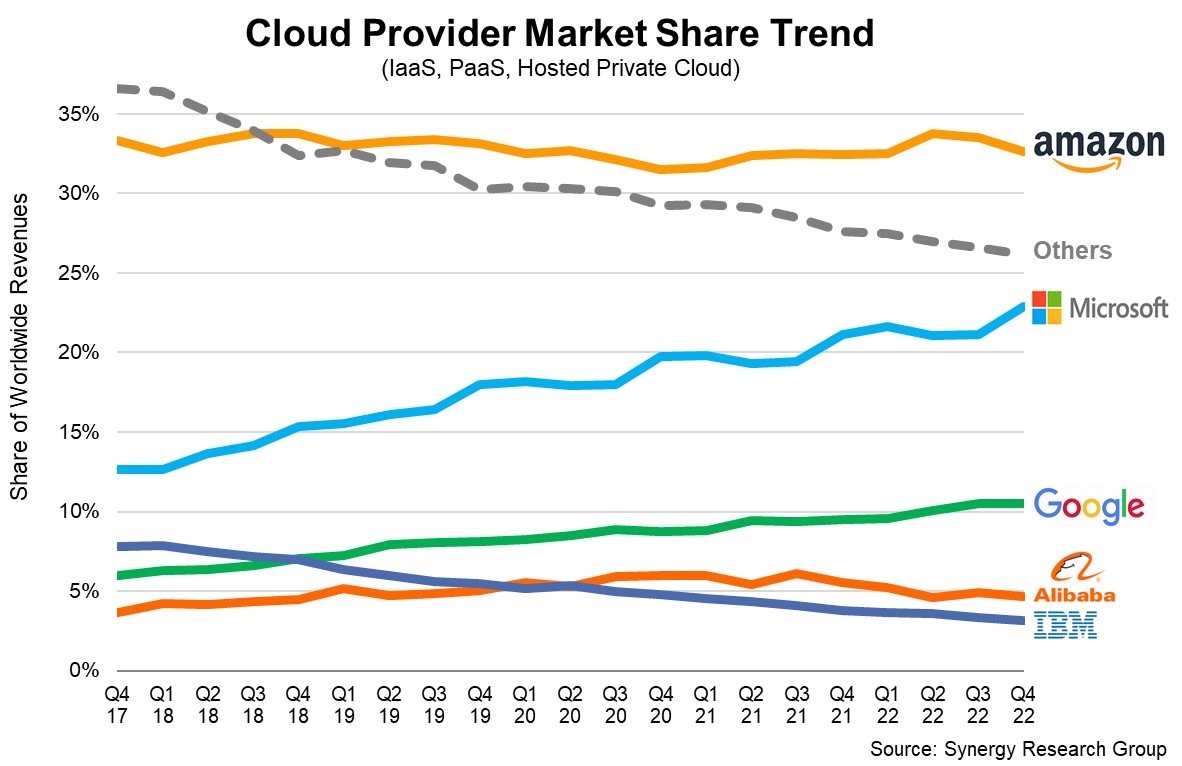
Trends and shifts in the market for Q2 2023 can be seen in the subsequent report, represented in the chart that follows:
Conclusion
Cloud service-based IT infrastructures continue to gain traction. Their affordability makes them a preferred choice for businesses over traditional hardware purchases.
















