It is impossible to fully understand the concept of the cloud itself without cloud architecture. That’s why it’s necessary to discuss it in detail.
Contents of Articles:
- Cloud Architecture Principles
- Cloud Categories
- Cloud Computing Levels
- Cloud Infrastructure Organization
Cloud Architecture Principles
When discussing cloud architecture, it is essential to imply a cloud computing model. There are different models — IaaS, PaaS, SaaS. In today's article, we will delve into the IaaS architecture.
The IaaS cloud is created from several physical modules connected by fast data transmission channels. It’s necessary to unify the management and transmission of large amounts of information. To be frank, there are hundreds or even thousands of modules in the data center of a cloud provider.
With the use of specialized virtualization software and the establishment of cloud infrastructure, users can access cloud resources without concerning themselves with the allocation of specific physical modules. In fact, the user does not care about the used modules, where his data is stored, and so on. The important thing is that the task is completed and the data remains intact.
Virtual machines are created in the IaaS cloud architecture. Guest OS and various apps can be installed by the user. It’s possible to use any OS in compliance with your demands.
Note. You can run several dozen virtual machines that are rented out on one hardware module.
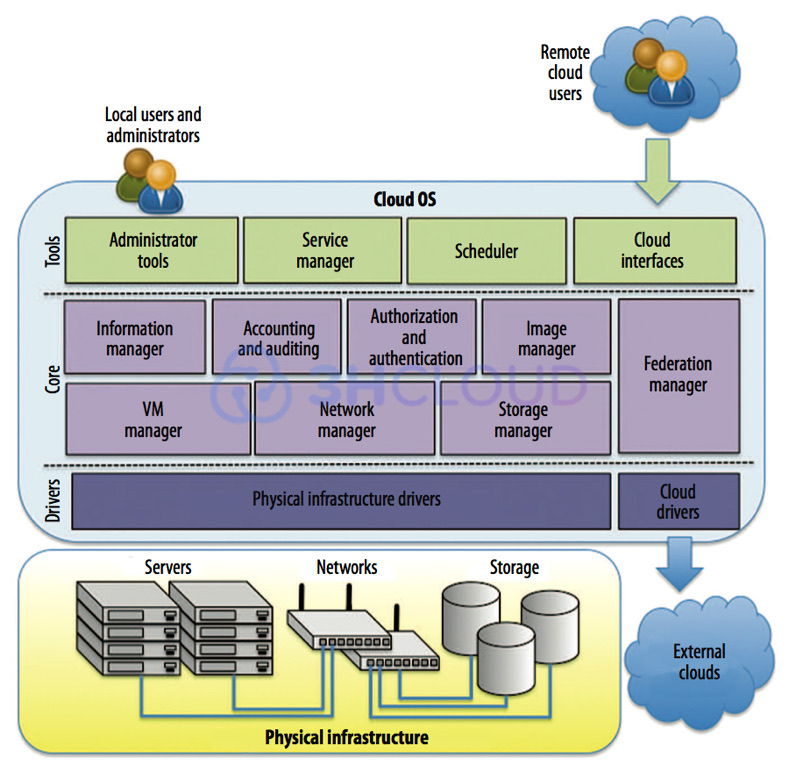
Most users do not need to know the full IaaS architecture but still consider the main points. There is a certain physical infrastructure consisting of servers, network equipment, and storage devices. A cloud operating system is running on this physical infrastructure.
As usual, the lowest level of any operating system is the drivers for interacting with hardware. Our cloud OS also has such drivers. These are physical infrastructure drivers. There are also cloud drivers. They are needed to connect to other, external clouds.
The core of the cloud OS consists of various dispatchers. There is a virtual machine manager (VM manager), Network manager, Storage manager, etc. Each of the dispatchers is responsible for its own part of the operating system in the IaaS architecture.
At the top of the system are various management tools. These are administrator tools, service manager, scheduler, cloud interfaces, and so on. Cloud users connect to it through the cloud interfaces. The interfaces can be different, but recently the web interface has been most often used.
Cloud Categories
According to the form of ownership, there are three forms of IaaS clouds:
- Public. They are used simultaneously by many different companies. Everything is simple here: there is a certain cloud provider who built a data center and provides its resources to everyone.
- Private. They are built by large companies for their needs.
- Hybrid. They use the best features of a public and private cloud. Imagine that a company has its own private cloud. But there are periods when private IaaS cloud architecture cannot cope with the increased load. In this case, a part of the resources is taken from the public cloud.
These categories of IaaS infrastructure are commonly utilized.
Cloud Computing Levels
There are the following levels:
- Client software is used to access cloud services, most often through a browser.
- Services are used through the cloud model.
- Applications that work through the cloud IaaS architecture and do not require installation on user computers.
- The platform layer combines a complete set of tools for deploying and using cloud computing.
- The Data Layer stores user data and provides access to it through the cloud interface.
- Infrastructure provides a virtualized platform through the cloud.
Cloud Infrastructure Organization
It is essential to have a clear understanding of the goals set for the architect when designing the IaaS cloud architecture. It will be better to use the private model for big companies. That is so even if it sometimes will not cover all the needs of the organization and periodically has to turn it into a hybrid. Such companies need full control over the processed data so that confidential data does not go beyond the companies.
For small and medium-sized companies, a public cloud model is ideal. If a company is just starting its activities, there is no need to buy physical servers. Just rent virtual ones and save a lot of money that can be spent more profitably.
You can virtualize existing servers and move them to the cloud, then disable the physical ones. As a result, the company will save some money. Virtual servers do not need to be repaired but you only need to pay rent on time, and the cloud provider will take care of the hardware.















